Standard Shaders (PBR)
Base Shader
This functionality is common to almost all of the ORL Standard-based shaders
All of the standard shaders have names beginning with Standard, from pure Standard to Standard Triplanar Effects and others
This page describes all of the properties that are shared between almost all of the Standard-family shaders, while other pages in this group describe settings specific to each one of the special variants
Shader Overview


The UI is broken down into multiple sections some of which you can probably collapse since you will likely not be touching them too often, e.g., "Advanced Features" and "Internal".
We will now go through every section, explaining the features it provides.
Optional Settings
Note that not all of the settings are always visible, some options will show and hide based on the textures/toggles you select
Main Settings

Note for Substance Painter Users
If you are an artist using Substance Painter - you can utilize the Unity HD Render Pipeline (Metallic) export tempalte for your textures. This will correctly map to what ORL Shaders expect.
- Main Color: Main tint color
- Albedo: The Main Texture, its tiling and offset will be used by all the textures in the material unless the texture slot provides its own tiling/offset parameters
- Mapping Space: Allows you to select between UV-mapped and Local Space/World Space aligned textures, which is useful for flat surfaces like Floors or Ceilings
- UV: Uses the first UV channel to display the texture
- Local Space: uses local coordinates on the provided X and Y axis to display the texture
- World Space: uses world coordinates on the provided X and Y axis to display the texture (useful for maintaining constant scale among many meshes)
- Triplanar: Uses a fast triplanar technique to display the texture. This mode does not need the mesh to have usable UVs, but it is not as fast as any other mode. The tiling is controlled by the X axis of the Albedo texture settings
- X Axis and Y Axis: Only visible when Mapping Space is not in UV or Triplanar mode. Allows to select which axis (X/Y/Z) to use for displaying the textures
- Masks: Texture containing Metallic/Smoothness and AO maps. By default uses this channel setup:
- Red: Metallic
- Green: AO
- Blue: Detail mask
- Alpha: Smoothness
- Metal/AO/Detail/Smooth selectors: Only visible when Masks texture is plugged in (see screenshots above). Allows you to select which channel to use for which map. E.g., you can remap to an unreal-style RMAO setup using these options
- Roughness Mode: Only visible when Masks texture is plugged in. Flips the Smooth channel to accommodate for roughness maps, useful for Unreal Engine assets
- Smoothness: Controls global smoothness level, uses this value across the whole material. Only visible when there is no Masks texture provided
- Smoothness Remap: Allows you to adjust the range of smoothness values of the provided Smoothness map. Very useful for reusing existing textures for a wide variety of effects
- Metallic: Controls global metalness level, uses this value across the whole material. Only visible when there is no Masks texture provided
- Metallic Remap: Allows you to adjust the range of metalness values of the provided Metal map. Similar in application to the Smoothness Remap
- AO Strength: Only visible when Masks texture is plugged in. Controls the strength of the provided Ambient Occlusion map
- Detail as Tint Mask: Only visible when Masks texture is plugged in. Utilizes the provided Detail texture to mask portions of the Albedo which will be tinted by the Main Color
- Normal Map: The Normal texture with the normal strength slider
- Flip Y (UE Mode): Only visible when Normal Map texture is plugged in. Flips the green channel of the normal map for DirectX-style normal maps, which are commonly found in something like Unreal Engine assets.
- Emission: Specifies that the object emits light
- Emission Map: The emission texture with the Emission Tint, you can leave the texture blank and just adjust the tint if you want the object to emit one solid color
Parallax
Parallax Cost
ORL Standard uses a parallax technique called Parallax Occlusion Mapping, which is a fairly expensive effect, and you generally only want it on materials that require parallax to look good, an example below is one such material
Parallax Material Example

Most parallax options are hidden until Enable Parallax is checked
- Enable Parallax: Toggles the special Parallax variant of the shader
- Height: The parallax heigh texture, MUST be set to linear ("sRGB" unchecked on the texture importer)
- Height Strength: Controls the strength of the parallax effect
- Height Ref Plane: Moves the reference plane of the texture up and down, will change the perceived distance of the effect from the surface (see video below below). 0 is neutral
- Steps: Controls the quality of the effect. Default settings will probably be fine, unless you're using very high height intensity value, which will expose the "layering" of the effect.
- Scaled Based On Angle: "Flattens" the parllax strength at grazing angles. This hals avoid strong layer artifacts.
Height Ref Plane adjustment
Details
Details section allows adding extra variety to the surface with its own set of mapping settings. There are two modes available for the source textures, which are described below. The effect is filtered by the Detail channel of the Masks Map from the Main Settings, which is Blue by default.
Packed Mode inspector vs Separated Mode inspector
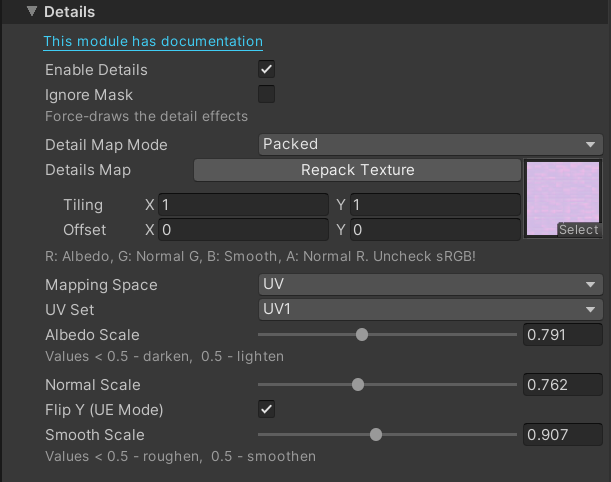

- Enable Details: Enables the effect
- Ignore Mask: Ignores the detail mask, which is usually taken from the Blue channel of the Masks Map texture from the Main Settings. This is useful if you are not using any masks texture at all
- Detail Map Mode: Controls how the details map is set up, which also changes its behaviour a bit
- Packed: This mimics HDRP detail map. You can read more about it here. This means you can use this mode with any HDRP assets out of the box. TL;DR: Albedo is packed into the Red channel, Smoothness into Blue, Normal into Green and Alpha
- Separated: A more classic mode, similar to the BIRP. Has separated slots for Detail Normals and Albedo + Smoothness, where Smoothness is packed into the Alpha channel of the Details Map.
- Details Map: The main details texture
- Details Normal Map: Only visible when Detail Map Mode is set to Separated. Allows specifying a bespoke normal map for detail
- Mapping Space: Allows you to select between UV-mapped and Local Space/World Space aligned textures, which is useful for flat surfaces like Floors or Ceilings
- UV: Uses the first UV channel to display the texture
- Local Space: uses local coordinates on the provided X and Y axis to display the texture
- World Space: uses world coordinates on the provided X and Y axis to display the texture (useful for maintaining constant scale among many meshes).
- X Axis and Y Axis: Only visible when Mapping Space is not in UV mode. Allows to select which axis (X/Y/Z) to use for displaying the texture
- Albedo Scale: Used to brighten and darken the texture, as only one channel is available. Values below 0.5 - darken, and above 0.5 - lighten the original Albedo.
- Legacy Albedo Mixing: Enables the legacy mixing mode, similar to Unity Standard Shader. This multiplies the main Albedo by Detail Albedo * 2. Only available when Detail Map Mode is set to Separated.
- Normal Scale: Controls the strength of the detail normal.
- Flip Y (UE Mode): Flips the Green channel of the detail normals. Allows the usage of DirectX normal maps, like the ones in the assets for Unreal Engine
- Smooth Scale: Allows to offset the smoothness using the details map. Values below 0.5 - make the surface more rough, above 0.5 - make it more smooth
Adding detail Normal and Albedo
VRChat Features
 VRChat Features controls
VRChat Features controls
- VRC Fallback: Sets the shader fallback mode as defined by the VRChat's Shader Fallback System
- Defaults to "Standard" which is the most fitting for the majority of shaders
- This option is available without needing to enable VRChat Features
- All of the available options are
- Standard
- Toon
- Hidden
- Transparent
- Cutout
- ToonCutout
- VRChat Features Enabled: Enables the VRChat features
- Hide from Main View: Controls whether the object should be hidden from the main player view
- In VR: Hides the object from the main player view in VR
- On Desktop: Hides the object from the main player view on Desktop
- Hide form Handheld Camera: Controls whether the object should be hidden from the handheld camera view
- In VR: Hides the object from the handheld camera view in VR
- On Desktop: Hides the object from the handheld camera view on the Desktop
- Hide from Mirror: Controls whether the object should be hidden from the mirror view
- In VR: Hides the object from the mirror view in VR
- On Desktop: Hides the object from the mirror view on Desktop
VRCLightVolumes

- Enable VRC Light Volumes: Enables the VRC Light Volumes module
There are currently no other controls for the VRCLightVolumes module as it directly replaces lighting data from the lightprobes.
Shading Mode

Shading mode settings fundamentally change how the base Diffuse and Specular calculations are done. Some effects might only work correctly in the Default shading mode.
- Shading Mode: Controls how the base shading is done
- Default: Default PBR Shading mode, expecting that the material is a regular solid surface: wood, metal, concrete, plastic, etc
- Cloth: Cloth-style Shading mode, when realtime lighting is used - cloth shading mode will make the material look like it has microsurface detail, adding a layer of sheen and wraparound lighting
Clear Coat settings
These are only visible if Shading Mode is set to Default
- Add Clear Coat: Adds a layer of clearcoat to the surface.
- Clear Coat Strength: Adjust the strength of clearcoat reflections and specular
- Use Clear Coat Mask: Enables texture masking of clearcoat areas. Useful if you only want some parts of your material to have clearcoat
- Clear Coat Mask: The mask texture to use for clearcoat. Only visible if Use Clear Coat Mask is checked
- Clear Coat Mask Channel: Picks which texture channel to use for masking the clearcoat effects. Only visible if Use Clear Coat Mask is checked
- Clear Coat Smoothness: Controls the smoothness of the clearcoat
Cloth Settings
These are only visible if Shading Mode is set to Cloth
- Custom Sheen Color: Allows customization of the sheen color
- Sheen Color: Tints the cloth sheen by this color
- Add Subsurface Color: Adds a very simple subsurface effect. Useful for velvet-y cloth effects
- Subsurface Color: Controls the tint of the subsurface ffect
Cloth Subsurface
It's important to note that this "Subsurface" effect is a very rough approximation based on the angle between the view, normal and the incoming light. It is not physically accurate, and thus there is no thickness mask or any other controls.
A proper subsurface implementation would be its own shading mode if it does get added at some point
Advanced Settings

- Culling Mode: Controls the culling applied to the mesh
- Back: Culls visible backfaces
- Front: Culls visible frontfaces
- Off: Renders in double-sided mode
- Render Type: Controls the render type of the material
- Opaque: Renders opaque objects
- Cutout: Renders cutout objects
- Transparent: Renders transparent objects with PBR-style alpha blending (similar to Unity Standard's Transparent mode)
- Fade: Renders transparent objects with simple alpha blending
- Custom: Exposes all the blending options for you to adjust manually
- Cutoff: Only visible when RenderType is Cutout. Controls the alpha cutoff value for the cutout render type
- Enable Vertex Lights: Allows objects to receive lighting from non-important lights. Please note that only dynamic objects will receive such lighting. This is a Unity limitation.
Depth
- Depth Write: Controls whether the object writes to depth
- On: Enables depth writing. As a rule of thumb - all opaque/cutout objects should write to depth
- Off: Disables depth writing, used for transparency
- Depth Test: Controls how the depth testing is performed, you generally never need to change this
GSAA
GSAA Example
GSAA, or Geometric Specular Anti Aliasing, helps avoid severe specular aliasing (often manifesting as "sparkles" visually) on metallic objects. It is enabled by default, as it is generally a very desirable effect
- GSAA Enabled: Toggles the effect
- GSAA Variance: Controls the change of the Normal direction required to be considered for GSAA filtering
- GSAA Threshold: Controls the cutoff of the variance which will be considered for GSAA filtering
- Include Normal Maps: Determines whether the input normals will include the per-pixel normal maps or not. Disabling this can clean up the "pixelated" look on highly detailed normals
Mobile Tweaks
- Force Box Projection: Enables support for Box Projected reflection probes on platforms that do not support it natively, e.g. Android (Oculus Quest). This is fairly expensive for mobile hardware, so use it sparingly
- Apply Mobile Color Correction: Enables color correction for mobile devices. As mobile platforms lack Post-Processing, it is often beneficial to use in-shader tone mapping to bring the look of your worlds closer to the Desktop version.
- Mobile Tonemapping Mode: Controls which algorithm to use for the color correction
- ACES: The default option and the most common tonemapper: ACES. Often produces results close to the Post Processing's ACES Tonemapper
- Unreal: The Unreal 3's ACES approximation. Faster to run but doesn't look as good
- Uncharted: The Uncharted 2's Filmic tonemapper approximation. It is also faster than ACES, but slower than Unreal
- Lift: The black point of the color correction
- Gamma: The gamma of the color correction
- Gain: The white point of the color correction
- Mobile Tonemapping Mode: Controls which algorithm to use for the color correction
Lightmapping

- Non-Linear Lightprobe SH: Enables higher quality lightprobe sampling which is more accurate and behaves much better in high-intensity lighting scenarios. Is recommended for use on PC platforms, but might be fairly expensive on mobile.
- Reflection Probe Occlusion (Previously Specular Occlusion): Controls the amount of Specular Occlusion applied to the reflection probe specular on this material. This helps limit the amount of "unity shine" which is often present on metallic surfaces (see comparison below). This applies to both lightmapped and non-lightmapped objects
- Realtime Shadow Specular Occlusion: Controls the amount of Specular Occlusion driven by the Realtime Shadows. This effect is not physically accurate but it can be useful to tame the strong specular on dynamically lit objects.
- Bicubic Sampling: Dramatically increases quality of the baked shadows, especially on the lower resolution lightmaps at a fairly small performance hit
- Baked Specular: Toggles the display of baked specular
- If the object is lightmapped - the Directional lightmap will be used. Recommended to be used with Bakery's MonoSH mode
- If the object is not lightmapped - the specular will be derived from Light Probes. Useful for avatars and other dynamic meshes
- Specular Roughness Mod: Allows you to influence the roughness of Baked Specular, which can sometimes be too intensive due to imperfections of Baked Specular direction
- Baked Specular Occlusion: Controls how much occlusion to apply to various sources of direct baked specular.
- If the object is lightmapped: this will adjust the intensity of the lightmap specular derived from the Directional lightmap.
- If the object is not lightmapped: this will adjust the intensity of the specular derived from lightprobes
- Global Illumination Tweaks
- Box Projection Contact Hardening: Enables box projection contact hardening, which improves the accuracy of reflections closer to the "surface" of the mesh
- GI Emissive Boost: Boosts the emissive contribution to the Global Illumination, can be useful for Realtime GI scenarios
- Ignore Realtime GI: Completely skips applying Realtime Lightmaps, which can be useful in scenarios where you want to only use Realtime GI for light probes
- Enable Bakery Features: Allows usage of bakery-specific features like RNM, SH or MonoSH lightmaps
- Bakery Mode: Specifies whether to use RNM, SH or MonoSH lightmaps for Baked Specular
- Bakery Non-Linear SH: Enables the Non-Linear SH sampling that can improve the contrast of the lighting on the mesh, especially with high-frequency normal maps
- Support Volumes: Enables Bakery Volume Support
- Assign Volume: Used to assing the volume textures to the material. Drag & Drop your volume object into that field to assign it
- Unset Volume: Removes the assigned volume from the material. Only visible if some volume data is set.
- Support Compressed Volumes: Enables support for compressed Bakery Volume textures. Only use this when enabling "Compress Volume" option in the Bakery bake settings.
- Support Baked Volume Rotation: Enables support for volumes rotated during baking. Requires special scripting support to work in VRChat.
- Support Runtime Volume Rotations: Enables support for rotating volumes in runtime. Requires special scripting support to work in VRChat.
Support package for volume rotations in VRChat is going to be available in the future.
Update Your Bakery
If you're not seeing MonoSH in your Directionality Mode dropdown when using bakery, you should update to the latest version! MonoSH is a new feature that was added in Bakery 1.9.0, it allows you to use a single directional lightmap to achieve a level of quality comparable to the old regular SH lightmaps (which used 3 separate textures) and it doesn't require any special adapters to work
Specular Occlusion in action
 Without Baked Specular
Without Baked Specular
 With Baked Specular
With Baked Specular
Stencils
 Stencil Controls
Stencil Controls
For more information on stencils - check out the Unity Docs
- Reference: Sets the stencil reference value to use with the Various Operations
- Comparison: Controls the comparison mode, common values: Always, Equal, NotEqual
- Pass Operation: Controls what happens when the stencil comparison passes. Common values: Keep, Replace, Zero
- Fail Operation: Controls what happens when the stencil comparison fails. Common values: Keep, Replace, Zero
- ZFail Operation: Controls what happens when the stencil comparison passes but the depth test fails. Common values: Keep, Replace, Zero
Internal
Debug Information
You do not have to adjust the settings shown in the Internal section, these are provided only for debugging
- DFG LUT: The DFG-multiscatter LUT texture used for the specular calculations
- RNM0/RNM1/RNM2: Bakery-specific texture slots for RNM and SH support
- Volume 0/Volume 1/Volume 2/Volume 3/Volume Mask: Bakery Volume textures
- Volume min: Bakery Volume minimum position (used for bounds)
- Volume Inv Size: Bakery Volume size (used for bounds)
LOD Crossfade
To add LOD Crossfade - simply select the Cutout variant of any Standard shader. This allows you to fade out the object as it gets further away when combined with an LOD Group component. Read more here.
You can also add support for LOD Crossfade to any shader by utilizing Configurable Shaders and adding the LODCrossfade module.
Examples
Here are some example material screenshots